The equations in matrix form are R = ˉx ˉy = cos θ − sin θ sin θ cos θx y Example 16 Rotate the line y = 5 x 1 an angle of 30° counterclockwise Graph the original and the rotated line Since 30° is π/ 6 radians, the rotation matrix is cos π 6 − sin π 6 sin π 6 cos πX2 − 2a a3 sec3 θa tan θ a 2 cos 2 θdθ = a 2 1 θ 1 1 θ 1 = a2 (2 sin 2θ) C = sin θ cos θ) C (1) 4 a2 (2 2 = 1 2a3 cos − ( xa x √ 2−a) 2a2x2 C Solution to (c) The term a2 − x2 suggests the substitution x = a sin θ,and this leads to integration of sec θ at the endTry IT(トライイット)のθ と θ+(π/2)の関係の映像授業ページです。Try IT(トライイット)は、実力派講師陣による永久0円の映像授業サービスです。更に、スマホを振る(トライイットする)ことにより「わからない」をなくすことが出来ます。全く新しい形の映像授業で日々の勉強の
Find X From The Following Equation Cosec P 2 8 X Cos 8 Cot P 2 8 Sin P 2 8 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Sin(π/2-θ)
Sin(π/2-θ)-Show that the distance d between the points P 1 and P 2 with spherical coordinates (ρ 1, θ 1, ϕ 1) and (ρ 2, θ 2, ϕ 2), respectively, is d = ρ 1 2 ρ 2 22 ρ 1 ρ 2 sin ϕ 1 sin ϕ 2 cos (θ 2θ 1) cos ϕ 1 cos ϕ 2Where sin 2 θ means (sin θ) 2 and cos 2 θ means (cos θ) 2 This can be viewed as a version of the Pythagorean theorem, and follows from the equation x 2 y 2 = 1 for the unit circle This equation can be solved for either the sine or the cosine




For 0 Less Than Theta Less Than Pi 2 Find Cos Theta If Tan Theta 5 6 Study Com
The numerator of the tangent function, the sin θ, is zero when θ = 0, ± π, ±2 π and so on At each of these sine values the tangent equals zero and is when a tangent graph line intersects the horizontal xaxisAs previously mentioned, the functions sin x and cos x are periodic with period 2 π sin(x 2 kπ) = sin x and cos(x 2 kπ) = cos x for any k ∈ Z Graphically, this means that once we have drawn a full period of each of the graphs of sin x and cos x, say in the interval 0, 2 π, we can obtain the full graphs of these two functions byWhere we used the sum formulas in Section 54 in the last line To show that the division formula holds, you can use the multiplication formula and that z 1 = z 1 z 2 z 2 Examples Carry out each of the following operations
Introduction to Systems of Equations and Inequalities;Where c 2 s 1 = 1, is called a Givens matrix, after the name of the numerical analyst Wallace Givens Since one can choose c = cos θ and s = sin θ for some θ, the above Givens matrix can be conveniently denoted by J(i, j, θ)Geometrically, the matrix J(i, j, θ) rotates a pair of coordinate axes (7th unit vector as its xaxis and the jth unit vector as its yaxis) through the givenSin2(θ)cos2(θ) = 1 (To the real showoffs try R dx sin2(ax) cos2(ax) = − 1 32a sin(4ax) x 8) As the exercise suggests, we first replace the sin and cos functions, then do some arithmetic sin2(θ)cos2(θ) = e iθ−e− iθ 2i 2 e e− 2 2 = 1 −4 eiθ −e−iθ 2 1 4 eiθ e−iθ 2 = 1 4 − eiθ −e−iθ 2
The fundamental identity cos 2 (θ)sin 2 (θ) = 1 Symmetry identities cos(–θ) = cos(θ) sin(–θ) = –sin(θ) cos(πθ) = –cos(θ) sin(πθ) = –sin(θFind x from the following equation cosec(π/2 θ) x cos θ cot(π/2 θ) = sin(π/2 θ) asked Jun 4 in Trigonometry by Daakshya01 ( 297k points) trigonometric functions1A (3) (c) R = 1 cos cos tan 2 2 π θ θ − θ 1M = 2 cos 2tan θ θ = 3 cos 2sin θ θ dR d θ = 2 2 4 2 1 3 cos sin cos 2 sin − θ θ − θ θ = 2 2 2 2 1 cos (3 sin cos) 2 sin θ − θ θ θ 1M dR d θ ≠ 0 when 6 π θ = ∴ R does not have a maximum at 6 π θ = 1A (3)



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions




Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Youtube
Show that for all real values of θ, the expression a sin 2 θ b sin θ cos θ c cos 2 θ lies between 2 1 (a c) − 2 1 b 2 (a − c) 2 2 1 (a c) 2 1 b 2 (a − c) 2 Medium View solution93 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities Two Variables;Sin 2 sin csc 2 csc cos 2 cos sec 2 sec tan tan cot cot nn nn nn θ πθθπθ θπ θ θπ θ = = = = = = Double Angle Formulas ( ) () 22 2 2 2 sin 2 2sin cos cos 2 cos sin 2cos 1 12sin 2tan tan 2 1tan θ θ θ θθθ θ θ θ θ θ = =− =− =− = − Degrees to Radians Formulas If x is an angle in degrees and t



Solve 2 Cos 2 Theta Sin Theta Le 2 Where Pi 2 Le The



Show The Trig Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Youtube
(cosθ)(tanθ) = sinθ for θ = 7 5π 61 cos2 θ sin2 θ = 1 for θ = 3 5π 62 1tan2 θ = sec2 θ for θ = 1775° 63 Verify that for θ = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, we have sinθ= 2 0, 2 1, 2 2, 2 3, and 2 4 respectively Although there is no theoretical significance to this pattern, people often use it as a memory aid to help recall5 Question Details SPreCalc6 503 Find sin t and cos t for the values of t whose terminal points are shown on the unit circle in the figure t increases in increments of π/4 t sin t cos tθ→π/2 cos2(θ) 1−sin(θ) Since at θ = π/2 the denominator of cos2(θ)/(1− sin(θ)) turns to zero, we can not substitute π/2 for θ immediately Instead, we rewrite the expression using sin2(θ)cos2(θ) = 1 lim θ→π/2 1−sin2(θ) 1−sin(θ) = lim θ→π/2 (1−sin(θ))(1sin(θ)) (1−sin(θ))



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



Inverse Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii
Find stepbystep Precalculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question Use identities to find the value of the expression if sin θ = 045, find cos (π/2 θ)Sin (π/2theta) = cos theta As π/2theta lies in the second quadrant so the answer will be in positive as it is lying in sin (second quadrant) and because of π/2 the sin will convert into cos thetaThe (π/2θ) formulas are similar to the (π/2θ) formulas except only sine is positive because (π/2θ) ends in the 2nd Quadrant sin (π / 2 θ) = cosθ cos (π / 2 θ) = sinθ




Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi Theta Cot 3pi 2 T



Sum And Difference Formulas For Sine And Cosine
=cos (π/2C/2) ∵ cos(π/2θ)= sinθ =sin C/2 = RHS (Hence Proved) (iii) tan (AB)/2=cot C/2 Solution Taking LHS tan (AB)/2 Putting the value of AB from (1) =tan(πC)/2 =tan (π/2C/2) ∵ tan(π/2θ)= cotθ =cot C/2 = RHS (Hence Proved)π °= And so with 4 π θ= we have ( ) 2 2 4 4 2 π π = ⋅ A = Problems 8 Find the area of a sector determined by a 196° angle in a circle of radius 6 9 Find the area of a sector determined by 3 5π radians in a circle of radius 2 THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUCTIONS For an angle θ in standard position, let (x, y) be a point on itsProportionality constants are written within the image sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, where θ is the common measure of five acute angles In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a rightangled triangle to ratios of two side lengths




Versine Wikipedia



Why Is Math Csc Frac Pi 2 Theta Sec Theta Math Quora
これを使ってθπの時と同じように考えていきます。 The sum of all the solution of the equation cot θ = sin 2 θ (θ = n π, n integer, 0 ≤ θ ≤ π) is A 2 3 π B π C 4 3 π D 2 π Medium Answer Correct option is A 2 3Cosθ sinθ cosθ sinθ 1 =cscθ (sin 2θ−cosθ) (sin2θcos2θ)=⋯ tan2θtan2θcot2θ= 1 1−sin2θ삼각함수의 각의 변환 두 번째예요 삼각함수 각의 변환 1 2n π ± θ, θ 에서는 θ 가 2n π θ 일 때와 θ 일 때를 공부해봤는데요 이 글에서는 θ 가 π ± θ 일 때와 일 때를 공부할 거예요 삼각함수는 기본적으로 sin, cos, tan의 세 가지인데, 거기에 π ± θ 와 로 네 개의 각이 나오죠? If sin θ = x Then putting sin on the right side θ = sin 1 x sin 1 x = θ So, inverse of sin is an angle Similarly, inverse of all the trigonometry function is angle Note Here angle is measured in radians, not degrees So, we have sin 1 x cos 1 x tan 1 x cosec 1 x sec 1 x tan 1 x




For 0 Less Than Theta Less Than Pi 2 Find Cos Theta If Tan Theta 5 6 Study Com



Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta Tan 5pi 2 Theta Cot 7pi
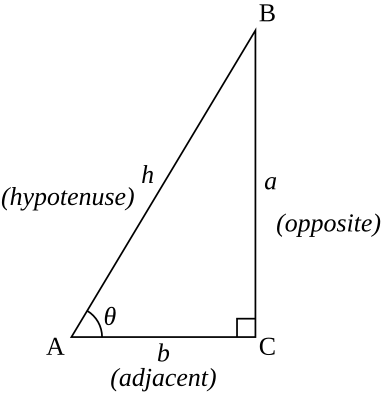
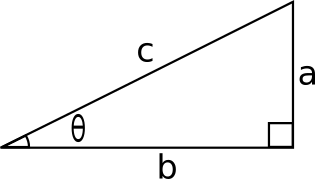
2 i(sin 2 cos 1 isin 1 cos 2) = r 1r 2 cos( 1 2) isin( 1 2);It is easy to see how the sine of an angle ( sinθ) varies as angle θ varies from 0 to 2π (One full cycle) In the unit circle shown, let angle θ or Arc AM vary from 0 to 360° or 2 π At any position that M has on the circle, draw a line perpendicular to the xaxis and call it MP , as shownAnswer (1 of 10) Sometimes it's easiest if you go back to the basic definitions Let's label the sides of a right triangle a, b and c, and the angle opposite a as \theta Then \sin \theta = \dfrac a c \cos \theta = \dfrac b c \tan \theta = \dfrac a b and of course a^2 b^2 = c^2 Usually



Oqz8s Mnpsgsqm




2 Assume 0 8 P 2 So That Sin 8 0 And Cos 8 0 If X Y Is Download Scientific Diagram
91 Systems of Linear Equations Two Variables;2 2 2sec 3 θ π So sin cos30 cos sin30 2 sin cos60 –cos sin60 (using the addition formulae for sin) 31 1 3 sin cos 2 sin cos 2 2 22 3sin cos 2sin 2 3cos (multiplying both sides by 2) 2 3 sin 1 2 3 cos xx x x xx x x x x x x Find real θ such that (3 2i × sin θ)/(1 – 2i × sin θ) is imaginary (a) θ = nπ ± π/2 where n is an integer (b) θ = nπ ± π/3 where n is an integer (c) θ = nπ ± π/4 where n is an integer (d) None of these Answer Answer (b) θ = nπ ± π/3 where n is an integer Hint Given,



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



Find X From The Following Equation Cosec P 2 8 X Cos 8 Cot P 2 8 Sin P 2 8 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
96 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination;Using a similar approach, we can find the six trigonometric functional values for θ = π/2, θ = π, and θ = 3π/2 as, The trigonometric functional values of angles coterminal with 0, π/2 , π, and 3π/2 are the same as those above, and the trigonometric functional values repeat themselves (eg, π and 3π are coterminal and sin (π) = sinThe trigonometric R method is a method of rewriting a weighted sum of sines and cosines as a single instance of sine (or cosine) This allows for easier analysis in many cases, as a single instance of a basic trigonometric function is often easier to work with than multiple are The R method is most often used to find the extrema (maximum and minimum) of combinations of trigonometric



Verify Sin Pi 2 Theta Tan Theta Sin Theta Youtube
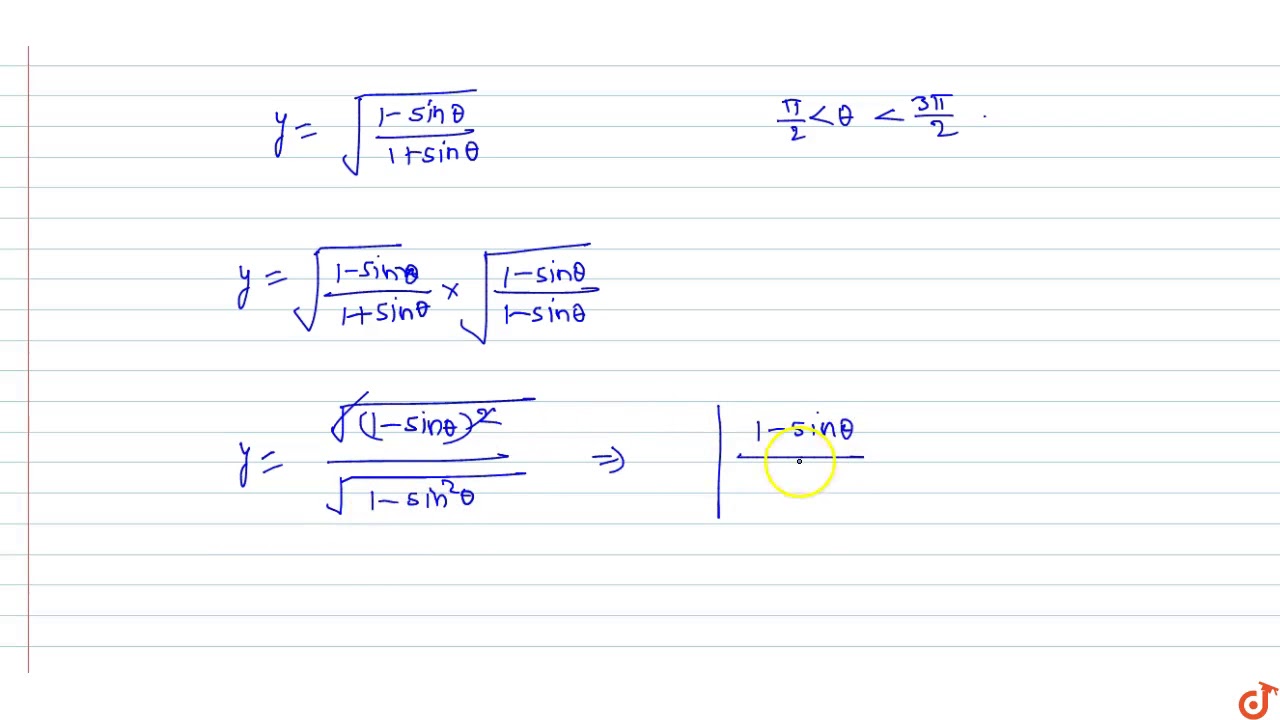



If Pi 2 Lt Theta Lt 3pi 2 Then Sqrt 1 Sin Theta 1 Sin Theta Is Equal To Youtube
97 Solving Systems with Inverses;92 Systems of Linear Equations Three Variables; Explanation using appropriate Addition formula ∙ sin(A± B) = sinAcosB ± cosAsinB hence sin( π 2 − θ) = sin( π 2)cosθ − cos( π 2)sinθ now sin( π 2) = 1 and cos( π 2) = 0 hence sin( π 2)cosθ − cos( π 2)sinθ = cosθ − 0
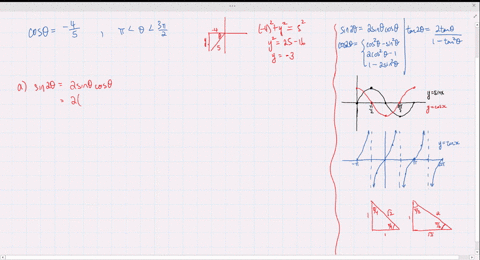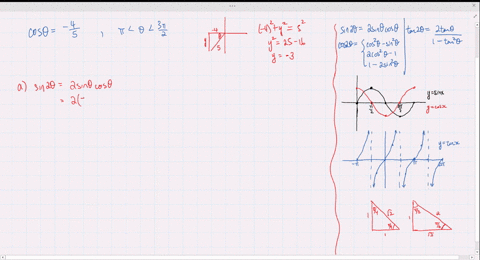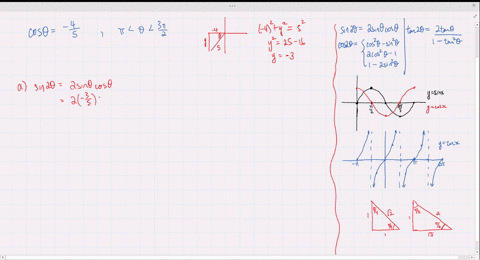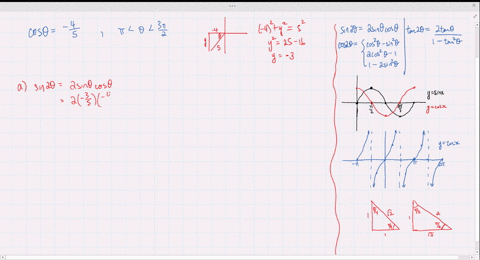



Solved Find The Exact Values Of Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta And Tan 2 Theta Subject To The Given Conditions Sin Theta Frac 2 3 Frac Pi 2 Theta Pi




Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle
95 Matrices and Matrix Operations;π/2−θの三角関数の公式 これらの公式を利用して、次の公式を証明してみましょう。 公式の証明は加法定理を用いておこなうこともできますが、今回は加法定理を学習していなくてもできる方法で行います。 sin(π/2−θ)=cosθ公式の導き方を覚えちゃえば楽勝だよ! /word_balloon ひとつひとつの公式を覚えていっても良いのですが結構大変です (^^;) 今回は三角関数の中でも、 や の形をした三角関数の公式とその導き方を伝えていきます。 記事の内容 ・θ+π/2,θπ三角関数の




Proof That Cos Theta Sin Pi 2 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange
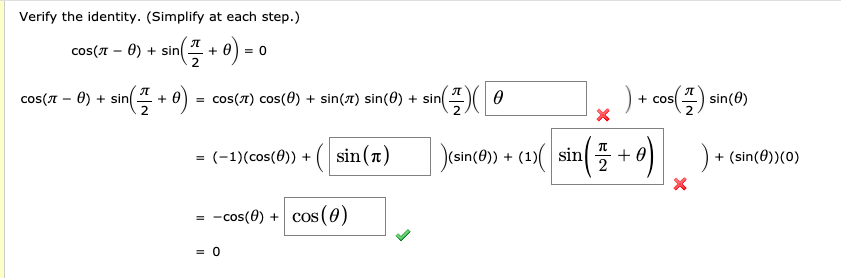



Solved Verify The Identity Simplify At Each Step Cos P Chegg Com
Like sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 and 1 tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ etc Such identities are identities in the sense that they hold for all value of the angles which satisfy the given condition among them and they are called conditional identities Trigonometric Identities With ExamplesClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If tan (picos theta) = cot (pi sintheta) than a value of cos ( theta pi/4 ) among the following isAssume θ = 90° {∵ 0 ≤ θ ≤ π/2} sin θ 2 cos θ = 1 ⇒ sin 90° 2 cos 90° = 1 ⇒ 1 = 1 Now, put θ = 90° in 2sin θ – cos θ,



Some Useful Trigonometric Identities




If Sin 8 3 5 And P 8 3p 2 Then What Is Tan 8 Quora
Let the lengths of the side opposite to the angle θ be 12 and the side adjacent to the angle θ be 35 so that cotθ=35/12 The length of the hypotenuse has been calculated using the Pythagorean theorem √(12²35²)=37 Then sinθ=12/37 cosθ=35/37 By the double angle formulas, sin2θ=2sinθcosθ =2⋅12/37⋅35/37= 840/1369= cos2θCos2 θ sin2 θ sin2 θ sin 2θ = 1 sin θ ie cot2 θ 1 = csc2 θ Summarising, cos 2θsin θ = 1 (6) 1tan 2θ = sec θ (7) cot 2θ1 = csc θ (8) Examples 1 Simplify the expression sec2 θ sec2 θ −1 sec2 θ sec2 θ−1 = sec2 θ tan2 θ = 1 cos2 θ sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1 sin2 θ = csc2 θ 2 Show that 1−2cos2 θ sinθcosθ = tanθ−定義 角 この記事内で、角は原則として α, β, γ, θ といったギリシャ文字か、 x を使用する。 角度の単位としては原則としてラジアン (rad, 通常単位は省略) を用いるが、度 (°) を用いる場合もある。 1周 = 360度 = 2 π ラジアン 主な角度の度とラジアンの値は以下のようになる:



If Pi 2 8 P And Sin 8 4 5 Find The Exact Value Of Cos8 And Cot8 Socratic



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Trigonometry Trigonometric Analysis Wikiversity



Biomath Trigonometric Functions




Ex 2 2 16 Find Sin 1 Sin 2pi 3 Chapter 2 Ncert Ex 2 2



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta Tan 5pi 2 Theta Cot 7pi 2 Theta Youtube




Find The Values Of The Other Five Trigonometric Fu Gauthmath




Trigonometric Functions Of Allied Angles Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin 2 Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos 2 Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan 2 Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin Left Frac 3




Overview 1 2 This Chapter Is Divided Up Into Two Main Sections Ppt Download
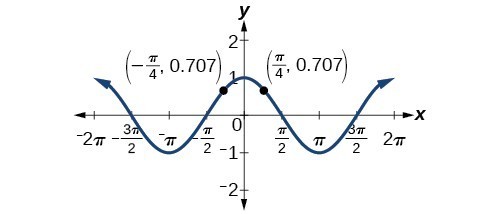



Solving Trigonometric Equations With Identities Precalculus Ii



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
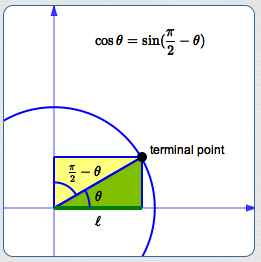



The Trigonometric Functions
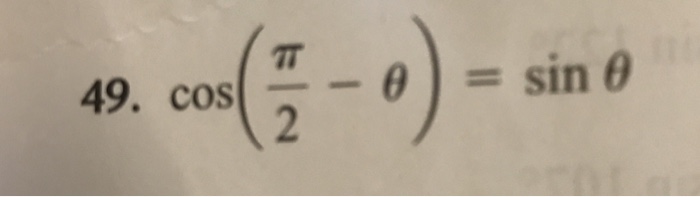



Solved Cos Pi 2 Theta Sin Theta Chegg Com



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
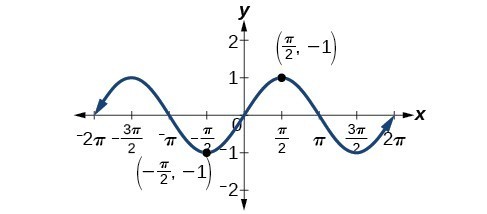



Solving Trigonometric Equations With Identities Precalculus Ii
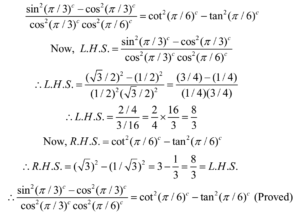



Trigonometric Functions Values Of Standard Angles And Their Use
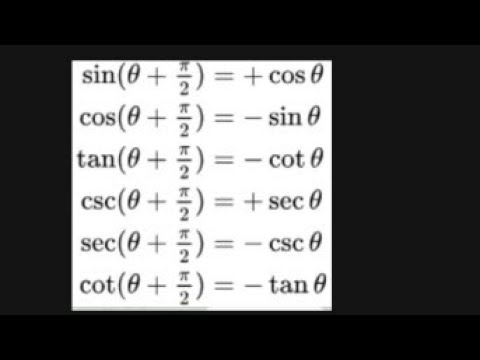



Proof Of Sin P 2 8 Cos8 Upto Cosec P 2 8 Sec8 Using Euler S Formula Youtube




स द ध कर क Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Sin Pi Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Cot 2 Theta
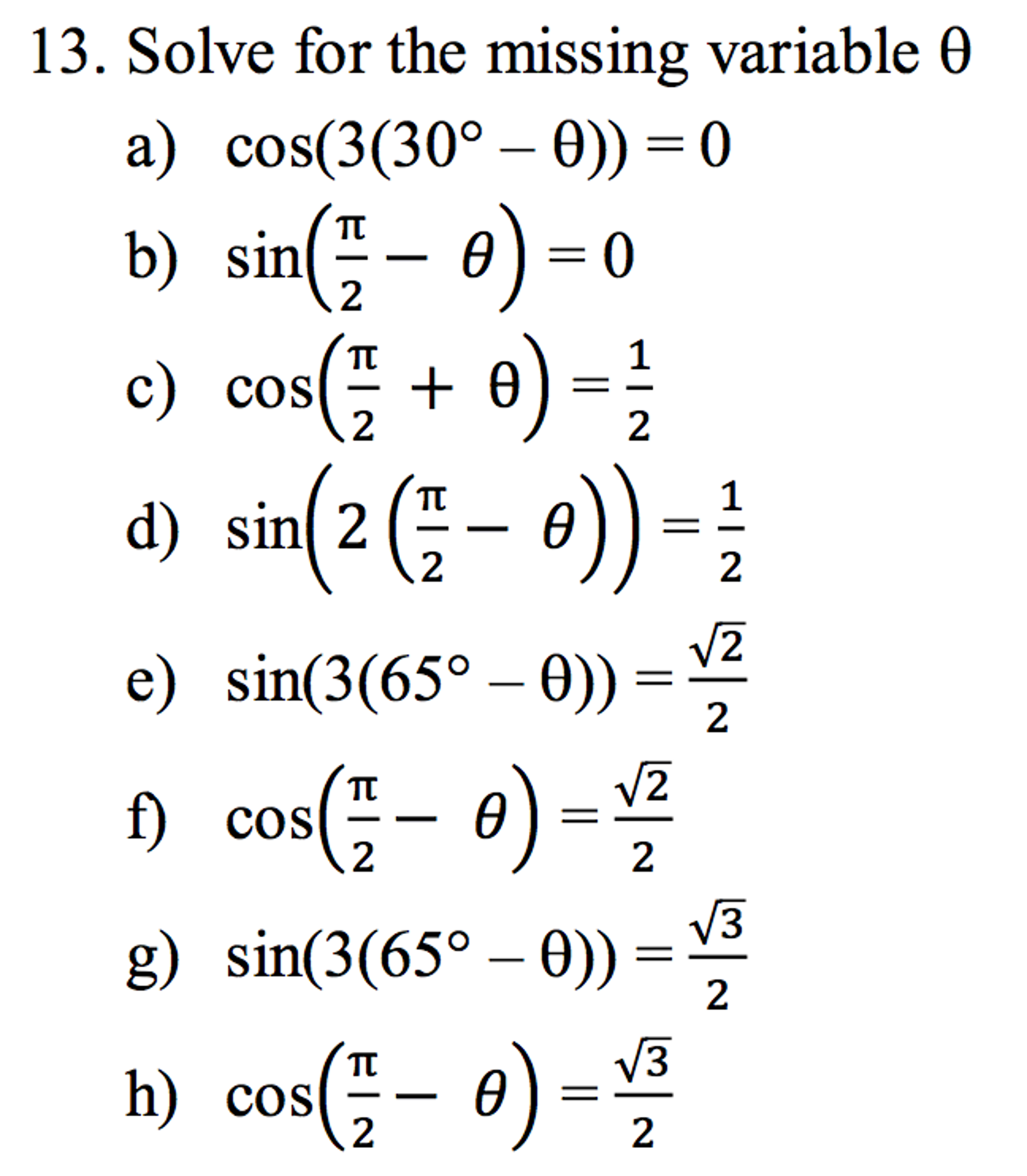



Solved Solve For The Missing Variable Theta Cos 3 30 Degree Chegg Com




How To Find The General Solution Of Sin Left Theta Frac Pi 6 Right Cos 3 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



1




Trigonometry




For 0 Less Than Theta Less Than Pi 2 Find Sin Theta If Tan Theta 5 6 Study Com




Geometric Proof Of Sin Frac Pi2 Theta Cos Theta For Theta Frac Pi2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Graphic Of G 8 P 2 4 Sin 2 8 8 2 1 Cos 8 For 8 0 P 2 Download Scientific Diagram




Show That Int 0 Pi 2 Sin P Theta Cos Q Theta D Theta Frac Sqrt Frac P 1 2 Sqrt Frac Q 1 2 2 Sqrt Frac P Q 2 2 P Q 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta Pi 2 Sin 2 Theta Pi Beth



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Show The Trig Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Youtube



Proofs Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia



What Is The Value Of Sin P 2 Theta Quora




If Sin P 4 Cos 8 And 0 8 P 2 Then 8 Homeworklib




If Csc Theta 2 06 Find Sec Theta Pi 2 Find The Exact Value Sin Pi 18cos Pi 9 Cos Pi 18sin Pi Brainly Com




Cos Pi 2 Theta Sec Theta Tan Pi Theta Sec 2pi Theta Sin Pi Theta Cot Pi 2 Theta Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



How Do You Prove Sin 2x Cos 2x 1 Example



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




If N Is An Integer And If Sin Theta 1 Prove That Theta 4n 1 Pi 2 Youtube
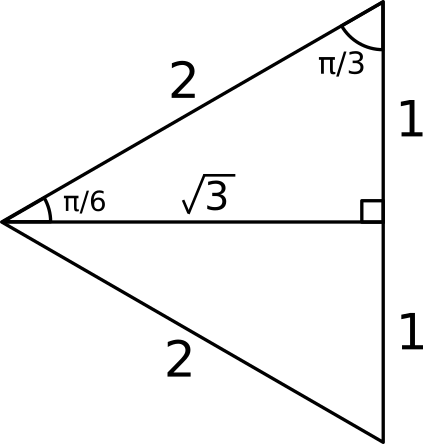



How Do You Evaluate Sin Pi 6 Socratic




Trigonometry Trigonometric Analysis Wikiversity



Inverse Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii




Solved Sin Theta Quad Cos Theta Quad Sin 2 Theta 2 Pi 2 Pi Find The Value Of The Determinant Begin Array C Sin




Sin P 2 8 Cos 8 Youtube




Solved Simplify Sin Pi 2 Theta Tan Theta 1 Chegg Com




Solve 11sin Theta 2 2 For A Value Of Theta When 0 Theta Pi 2 Socratic



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
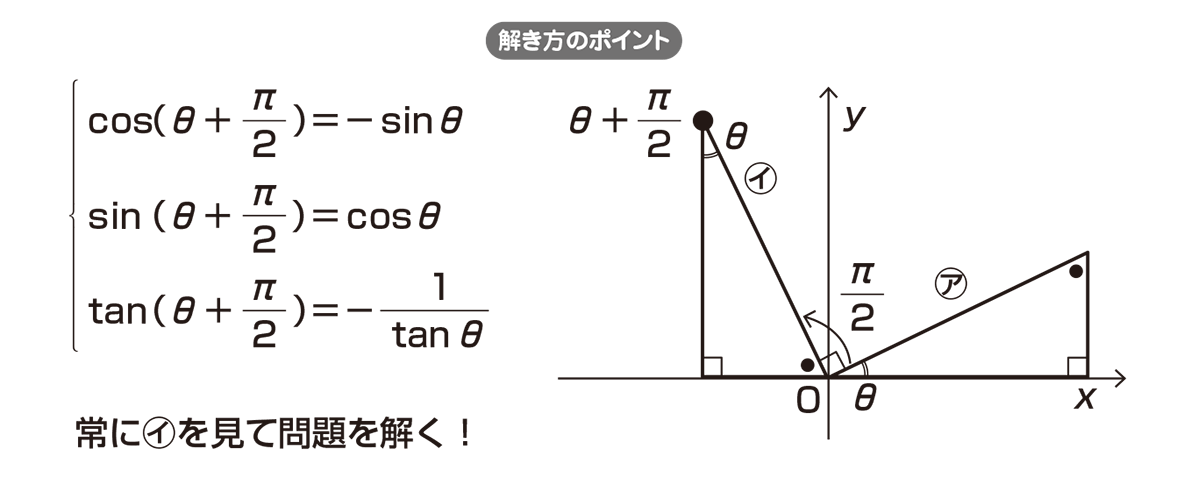



高校数学 8 と 8 P 2 の関係 映像授業のtry It トライイット
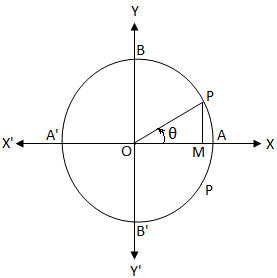



Sin Theta Equals 0 General Solution Of The Equation Sin 8 0 Sin 8 0




Given Sin A 5 13 Pi 2 Lt A Lt Pi And Tan B Sqrt 13 Pi 2 Lt B Lt Pi What Is Tan A Brainly Com



3
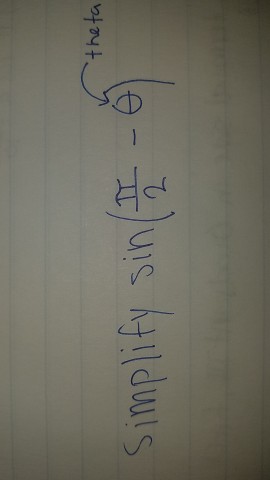



Solved Simplify Sin Pi 2 Theta Chegg Com
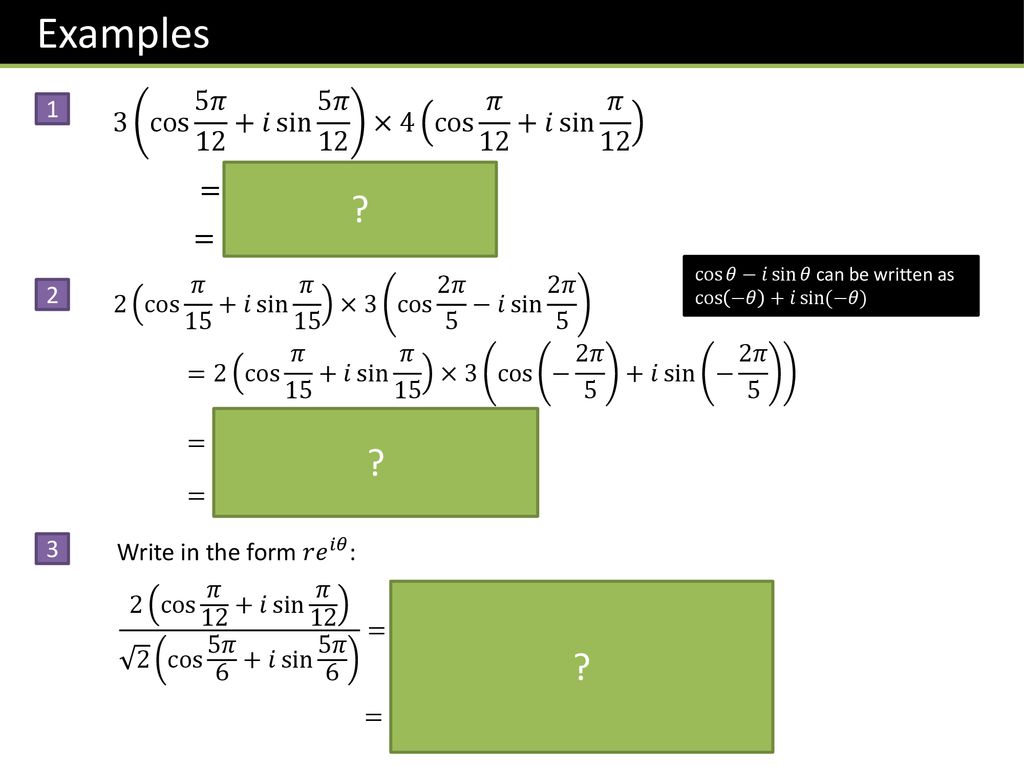



Corepure2 Chapter 1 Complex Numbers Ppt Download
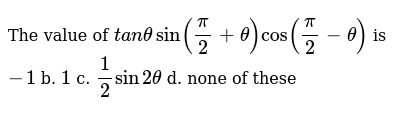



The Value Of T A Nthetasin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Is 1



1
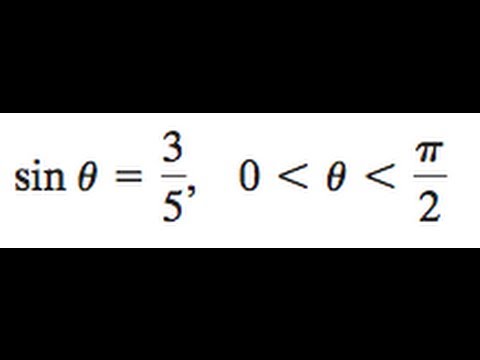



Find The Double Angle And Half Angles Of The Sin And Cos Of Sin Theta 3 5 Youtube




Proofs Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia




Why Is Cos Pi 2 Theta Sin Theta




bestpict8tek 上 Tan P 2 8 Tan Pi 2 Theta




Trigonometric Identity Review Trigonometry Identities Reciprocal Identities Sin 8 Cos 8 Tan 8 Quotient Identities Tan 8 Cot 8 Ppt Download



Biomath Trigonometric Functions




Solved Given Sin Theta Square Root 3 3 And 3 Pi 2 Chegg Com




If Cos Theta 0 8 Find 1 Sin Pi 2 Theta Brainly Com



1



Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions




Solved If Sin Theta 3 4 0 Theta Pi 2 Find The Exact Chegg Com



List Of Trigonometric Identities




Sin Pi 2 X Sin Pi 2 Theta Youtube
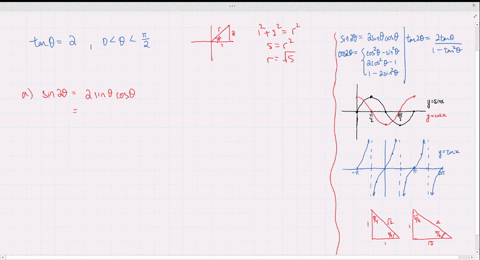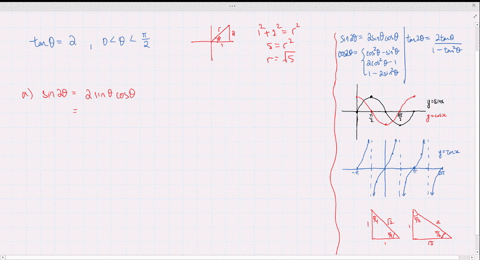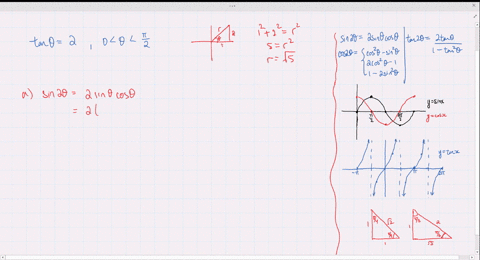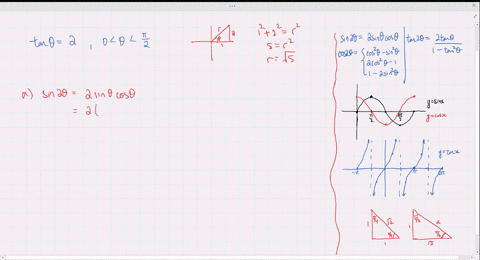



Solved Find The Exact Values Of Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta And Tan 2 Theta Subject To The Given Conditions Cos Theta Frac 4 5 Pi Theta Frac 3 Pi 2



M7ae8czsw4qdqm



Sine Function Sin X
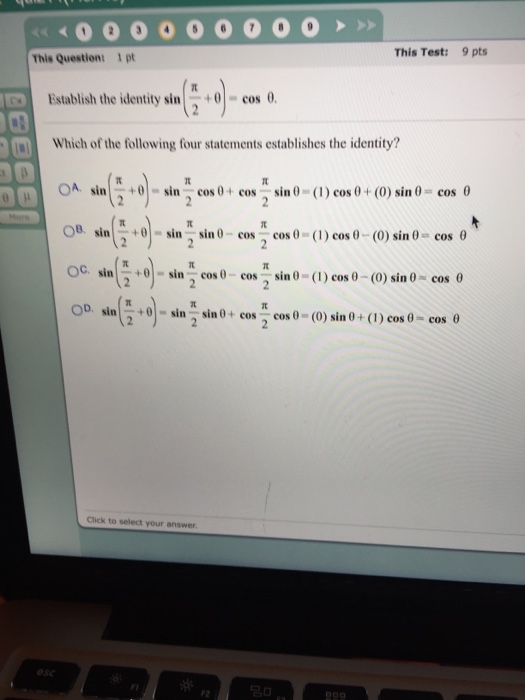



Solved Establish The Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Chegg Com
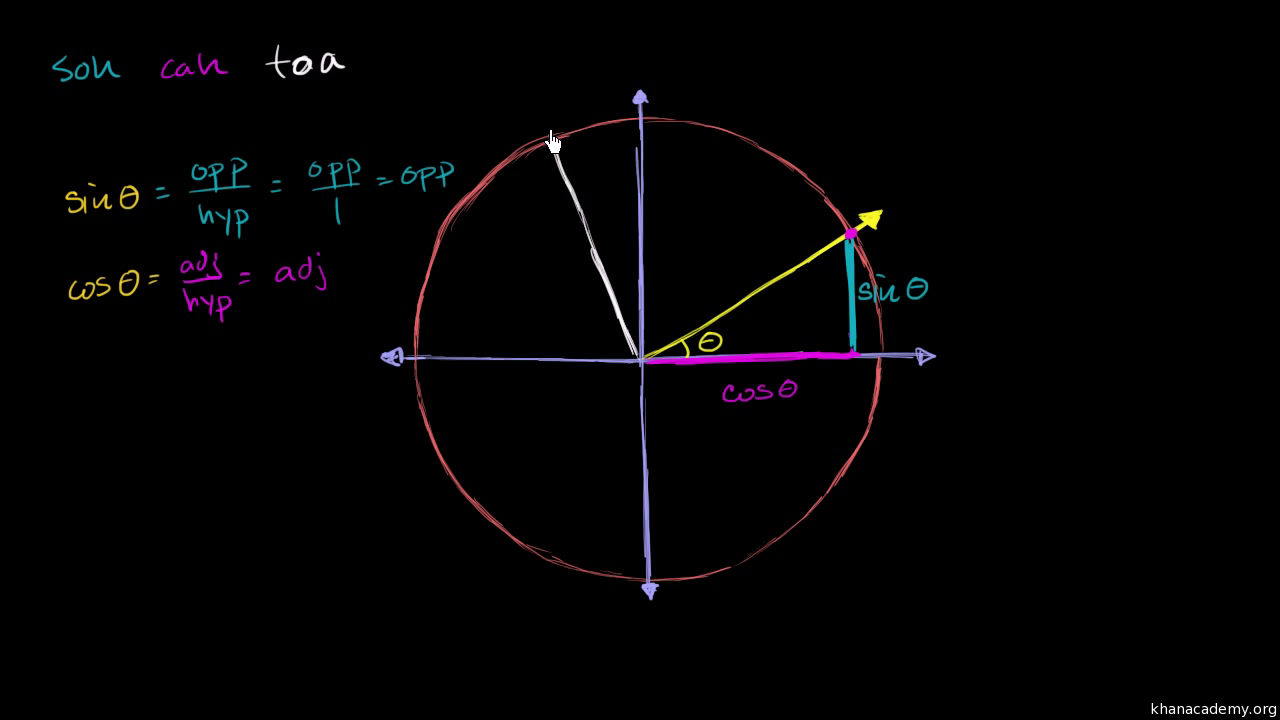



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy
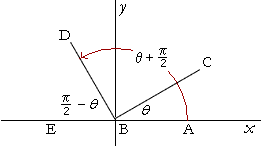



Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions
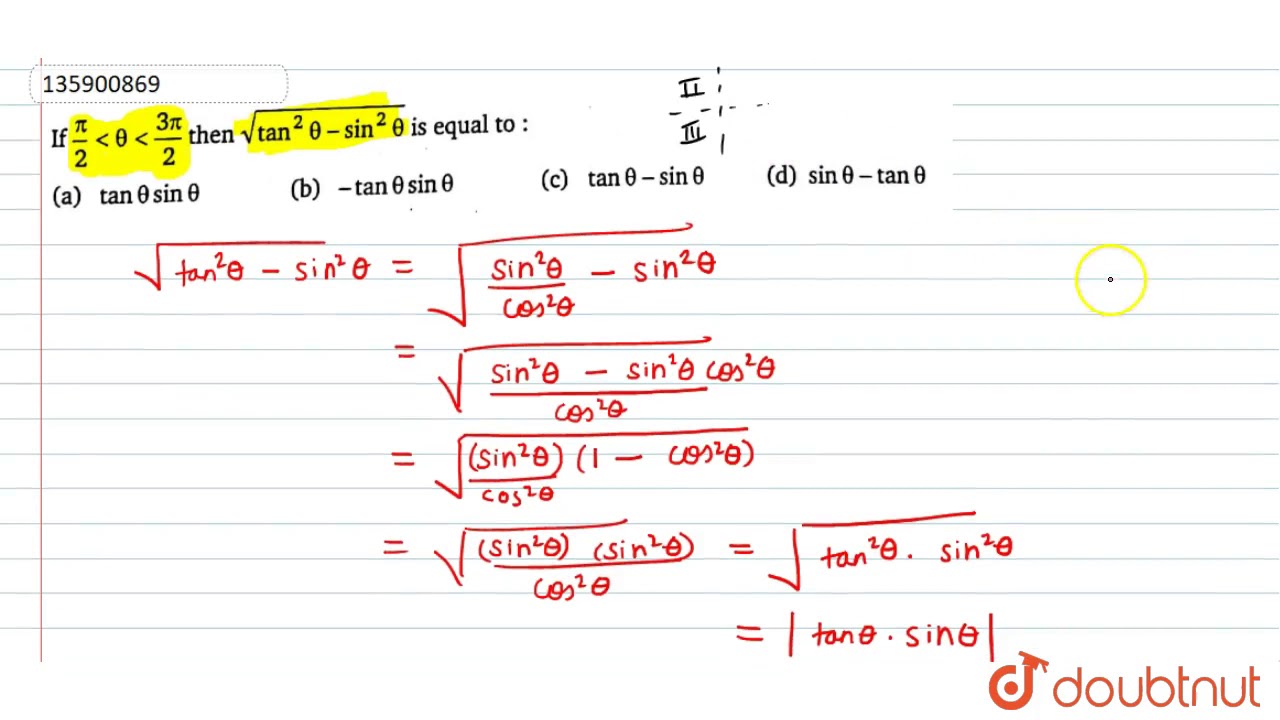



If Pi 2 Lt Theta Lt 3pi 2 Then Sqrt Tan 2 Theta Sin 2 Theta Is Equal To Youtube




Solved Prove That Frac Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Sin Pi Theta Cos Left Frac Pi



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle




Period Of Sin 2 Theta Is A Pi 2 B Pi C 2pi D Pi 2



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿